Using Google Sheets as your CMS


Spreadsheets. They are everywhere.
Managers especially seem to love them, which is why the world properly would stop functioning without them.
Like some twisted version of Murphy's law, it seems that anything that can fit into a spreadsheet eventually will end up in a spreadsheet.
This can result in abominations like a Microsoft Excel database for Covid-19 results.

Well, following in the spirit of using spreadsheets other ways than intended, I thought - what if we could use a Google Sheet as a CMS?
Hold on. Hold on. Lower your pitchforks and torches – this is merely a proof of concept to see how it could work. However... there might be some use cases for this – stick around to the end and find out.

So first thing first, how do we do it in a performant way? We could set up a script to generate a static site, which is something other developers also have played around with before.
However, we don't want to have to trigger a build each time we push a change in our sheet. We want to be able to use SSR, ISR, or CSR in a performant way.
What we want to do is decouple our Google Sheets so that it only works as a CMS and not a database.
Luckily, decoupling data is where Enterspeed really shines.

So let's get to it.
Step 1: Set up a Google Sheet
First, start by creating a Google Sheet. In our example, we're going to make a list containing all the movies from the best movie series in the world.
No, not Marvel or Star Wars. I'm of course talking about the one and only: Olsen Banden (The Olsen Gang).

The list contains the following columns:
- The number it has in the series (Number)
- The movies name (Name)
- Which year it was produced (Year)
- A link to the movie cover image (Image)
- A link to its IMDB page (IMDB)
- A short description (Description)
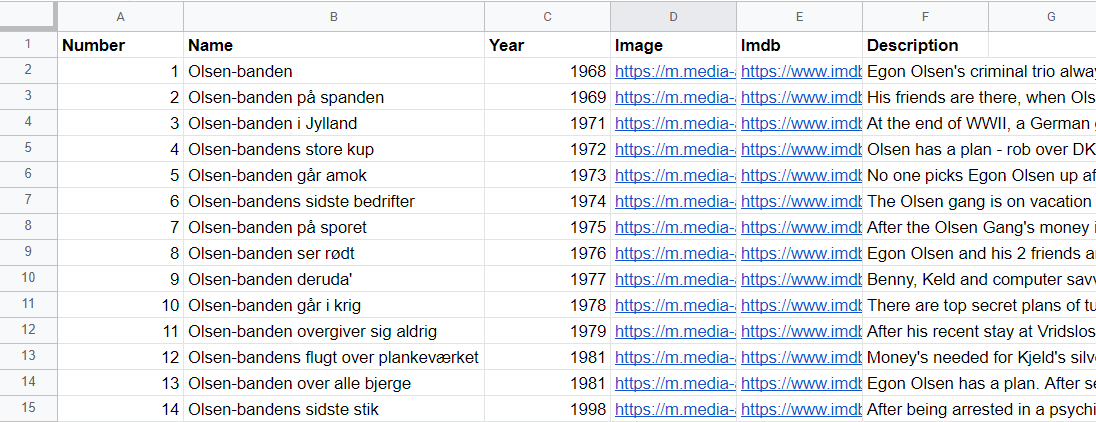
All content above is shamelessly copied from IMDB.com.
Now that we have all of our data, it's time for step 2 – setting up a script that ingests all the data into Enterspeed.
Step 2: Set up a Google Apps Script
Inside your Google Sheet, click on Extensions and select Apps script.
First, we create a function called ingestToEnterspeed.
Next, we declare two const to make the code easier to read:
- sheet which equals SpreadsheetApp.getActiveSheet() – this grabs our active sheet.
- sheetData which equals sheet.getDataRange().getValues() this grabs all the data from the active sheet.
Now, we take our sheetData-const and run a forEach function. We grab the index (i) of each, so we can:
- Skip the first row, since this is the header
- Know which row number to grab data from
Since our row numbers, unlike our index, don't start at 0, we declare a const called rowNumber which equals i + 1.
Next, we declare a const for the ingest URL to Enterspeed (ingestUrl). The part after /v2/ will be our originId inside Enterspeed and needs to be unique.
Since we're only going to be ingesting "Olsen banden"-movies, we will simply use "olsen-banden-" + the movie's number in the series - here found in column A. We could also have made a function that grabs the sheet name and combines it with the row number instead, to make it more dynamic.
The function we use to grab the cells content is: sheet.getRange('A' + rowNumber).getValue() – this takes the active sheet, finds the defined column for the defined row number and gets the value.
Now, we create an object called payload, which specifies what we will send to Enterspeed.
In the object, we need to define three properties:
- A type (in our case we simply call it 'movie')
- A URL, if we want it to be routable (if not, we can simply write null)
- Properties, which is our actual content
Our URL follows the same pattern as our originId "olsen-banden-" + the movie number.
Inside the properties object, we define all the data which we wish to use. The name of the keys can be whatever you like – to keep it simple we just matched the name of our columns.
Then we use the same function as before to grab the content from the cell we want.
Once we have defined our data (payload), we need to make an options object, which we will use in our fetch function.
Create a method property and set it to post. Then create a headers object where you define a x-api-key property. Insert the API key for your data source, which you have created inside Enterspeed. Lastly, create a payload property and insert JSON.stringy(payload).
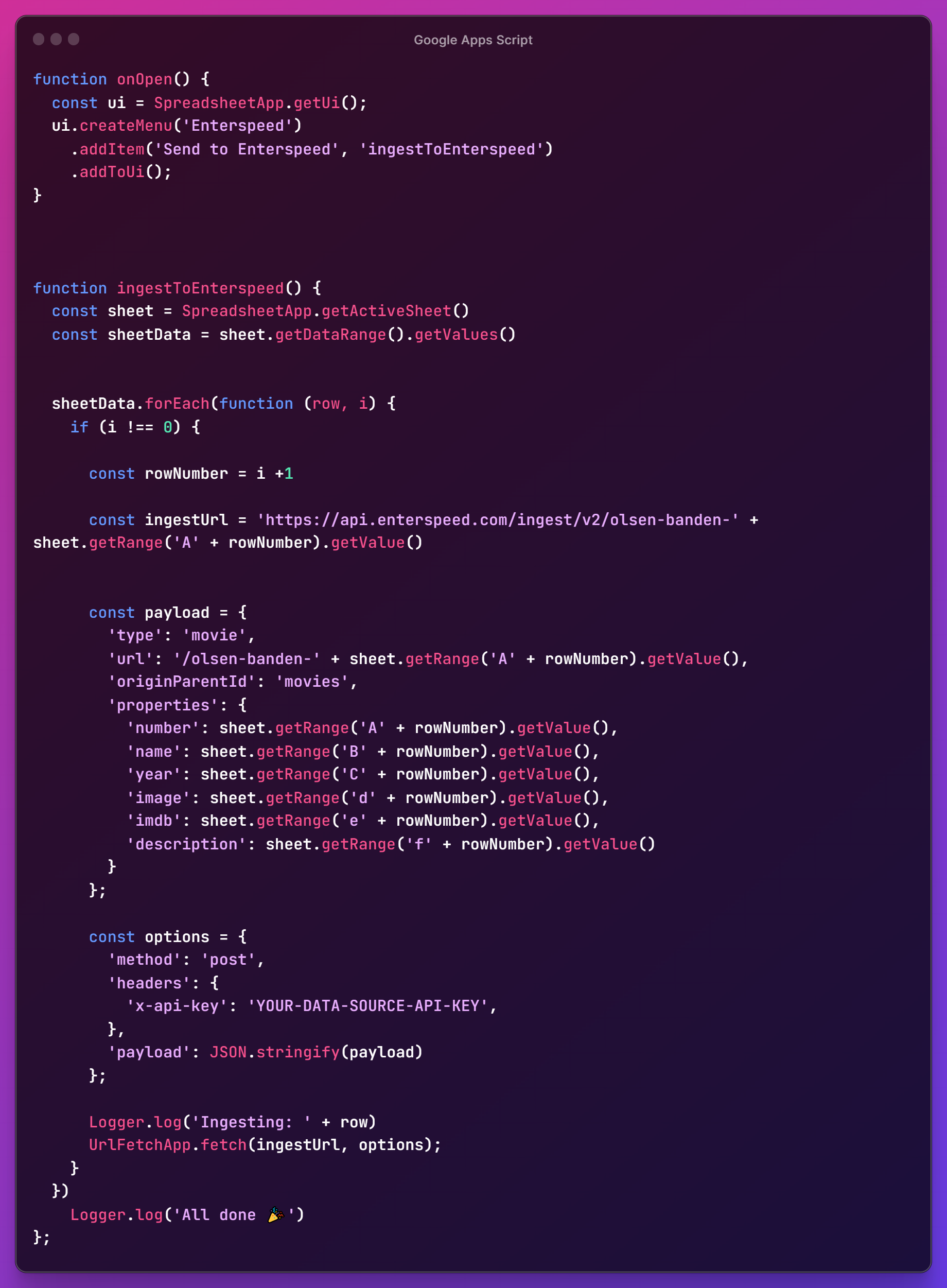
Next, for 💩 and giggles we can choose to log out each row inside Google Apps Script, to see what's going on, using Logger.log('Ingesting: ' + row).
Now, it's time to ingest the data using the build-in UrlFetchApp. Use the fetch method and set ingestUrl and options as parameter: UrlFetchApp.fetch(ingestUrl, options);
Click Save project and then click Run. You should now be able to see your content inside Enterspeed. Hooray 🎉
As a bonus, we can create a function that adds a menu item to your Google Sheets menu. This makes it easier to ingest data from the sheet.
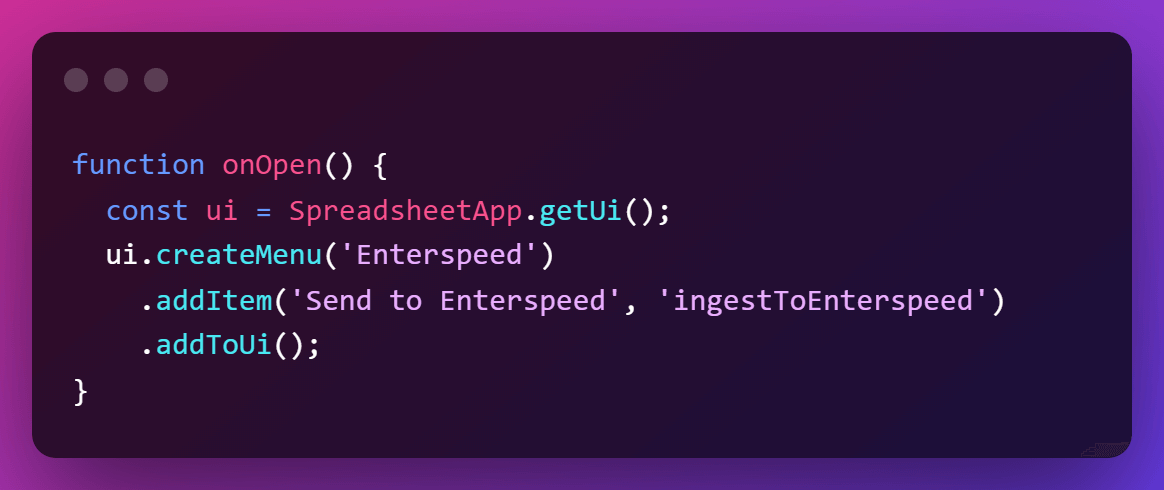
Google Apps Scripts even support triggers, which means you can set it up to ingest at time-driven events. That's pretty neat.
Next, we need to ingest a parent source into Enterspeed, which acts as a parent for all our movies.
Step 3: Ingest a parent source
Since we want to create a list of movies, we need to have each individual movie attached to a parent.
You might have noticed that we added "originParentId": "movies" in our Google Apps script. This is the one we're going to create.
We could add many interesting details to this source entity, e.g., a description of the movie series, trivia, etc. But for now, we will simply ingest an empty source entity into Enterspeed since it only needs to act as a parent.
So bring out your favorite API platform, e.g., Postman or Insomnia, and ingest an empty source entity into Enterspeed with the originId "movies": The URL should look like this: https://api.enterspeed.com/ingest/v2/movies
Remember to add your source API key as a header using the "X-Api-key"-key.
Awesome. Now that we got all of our data into Enterspeed, it's time to create a schema that generates the view we wish to use.
Step 4: Create a schema in Enterspeed
Open Enterspeed and create a new schema.
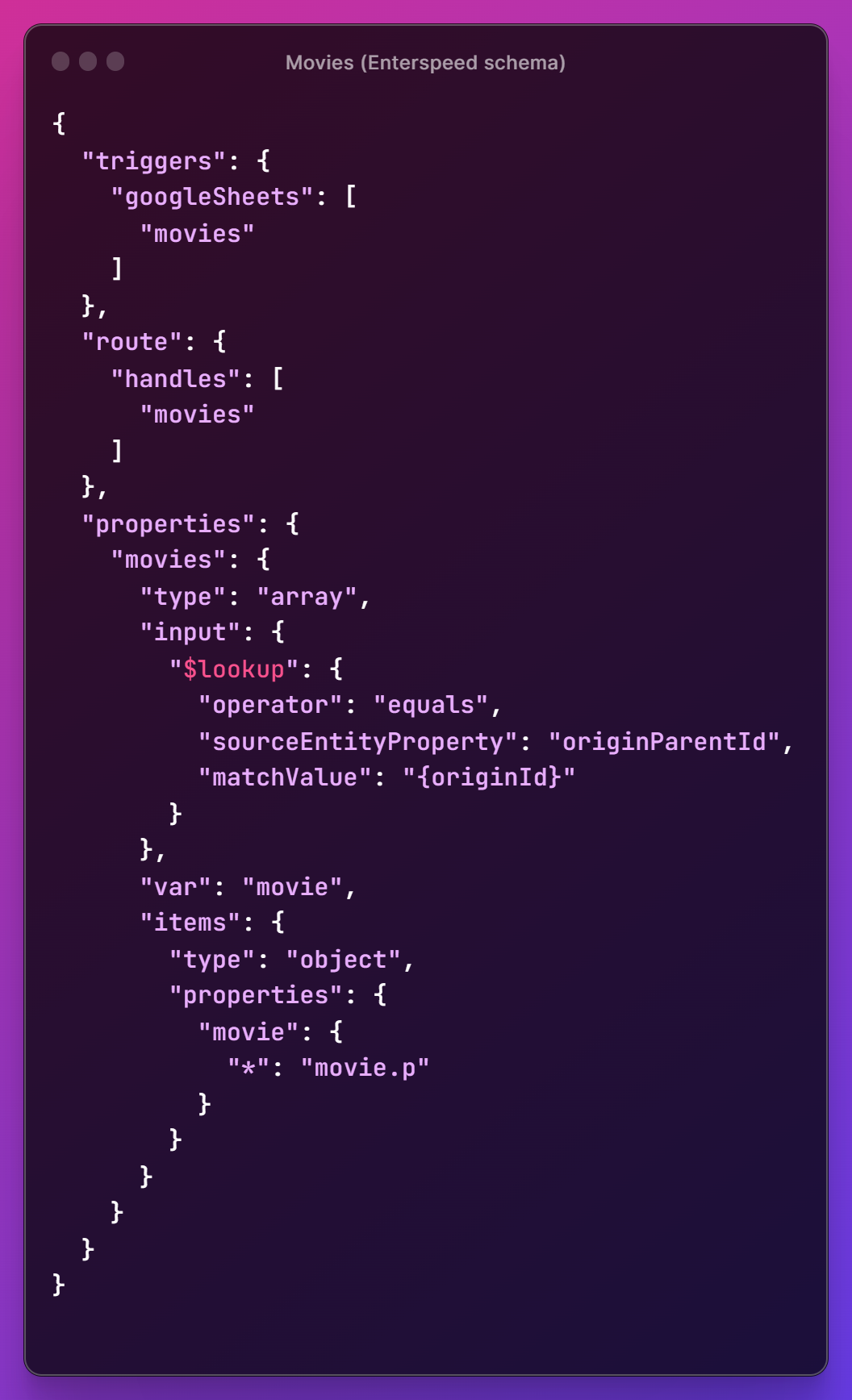
We're going to create a collection schema, which generates a single view for all the movies.
Since we have ingested all of our rows individually (with the URL property), we also have the option to make separate pages for each movie.
However, for now, we will simply make a collection schema.
We start by setting up our triggers, where we define which data source it should use - and which source entity type (here, we use the "movies"-type which we just ingested in our "parent" source entity).
We then choose how we should be able to "get the content" – this can be either via a handle or via a URL. In our case, we choose a handle called movies.
In the properties-object is where we define the actual content. We create a property called movies, which has the type array. In the input property, where we define the items we want to work with, we look for source entities with an originParentId that matches our originId (the "parent" source entity - movies).
For ease of use, we set the collection iteration variable name to movie instead of the default item using the var property.
Under items, which are used for mapping results, we choose to grab all the data and wrap them in an object called movie. We're able to grab all the data by using dynamic mapping.
That's it. Then we save the schema and deploy it to the environment we wish.
All that's left now is to fetch the data from the frontend
Step 5: Fetching the data
Now to actually show the data.
We fetch it using the Enterspeed Delivery API. We call the URL and add the handle we wish to fetch (here movies): https://delivery.enterspeed.com/v1?handle=movies
In our headers, we insert our Environment Client API key in the X-Api-key property.
Afterward, we iterate over all the movies and insert them into a card component (in this case we have used Bootstrap).
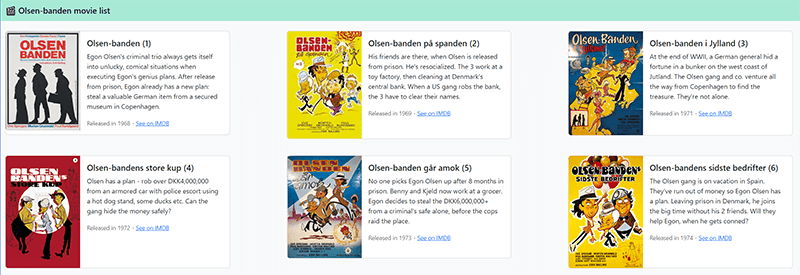
Voilà. We have successfully used Google Sheets as a CMS – but is this merely a proof of concept, or?
Google Sheets as a CMS – madness?
So could Google Sheets work as a CMS? In my opinion, yes.
Now, I know what you're thinking: "Madman! You're a madman! No man, developer, or client should use Google Sheets as a CMS!"
But oh, I've chosen my words carefully.
(P.s. if you don't get the reference – here you go).
Which CMS you should use all depends on the use case. Should you use Google Sheets for a blog? Properly not. A full fledge company website? Also no.
But say you are a small café, that often switches up its menu and wants to display the dish of the day. Or a small soccer club, that wishes to showcase all their players. Then yes, it could definitely work.
Since we decouple the data from the actual Google Sheets, it doesn't really matter performance-wise where you edit your data.
Also, Enterspeed allows you to transform and combine multiple data sources, which means you could use Google Sheets only for a small section of your site – e.g. your team section.
So the moral of the story is – once you have decoupled your data, it doesn't really matter how/where you edit it.

I hope you enjoyed the article. You can find all the code used here: https://github.com/enterspeedhq/enterspeed-demos/tree/master/vanilla-js-google-sheets

Loves optimizing and UX. Proud father of two boys and a girl. Scared of exercise and fond of beer.
